Phishing
Phishing is a type of cybercrime in which a sender seems to come from a genuine organization like PayPal, eBay, financial institutions, or friends and co-workers. They contact a target or targets via email, phone, or text message with a link to persuade them to click on that links. This link will redirect them to fraudulent websites to provide sensitive data such as personal information, banking and credit card information, social security numbers, usernames, and passwords. Clicking on the link will also install malware on the target devices that allow hackers to control devices remotely.
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack
A man-in-the-middle attack is a type of cyber threat (a form of eavesdropping attack) in which a cybercriminal intercepts a conversation or data transfer between two individuals. Once the cybercriminal places themselves in the middle of a two-party communication, they seem like genuine participants and can get sensitive information and return different responses. The main objective of this type of attack is to gain access to our business or customer data. For example, a cybercriminal could intercept data passing between the target device and the network on an unprotected Wi-Fi network.
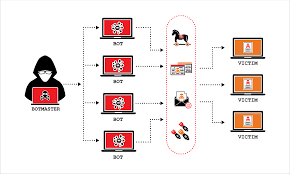
Distributed denial of service (DDoS)
It is a type of cyber threat or malicious attempt where cybercriminals disrupt targeted servers, services, or network’s regular traffic by fulfilling legitimate requests to the target or its surrounding infrastructure with Internet traffic. Here the requests come from several IP addresses that can make the system unusable, overload their servers, slowing down significantly or temporarily taking them offline, or preventing an organization from carrying out its vital functions.
Brute Force
A brute force attack is a cryptographic hack that uses a trial-and-error method to guess all possible combinations until the correct information is discovered. Cybercriminals usually use this attack to obtain personal information about targeted passwords, login info, encryption keys, and Personal Identification Numbers (PINS).
SQL Injection (SQLI)
SQL injection is a common attack that occurs when cybercriminals use malicious SQL scripts for backend database manipulation to access sensitive information. Once the attack is successful, the malicious actor can view, change, or delete sensitive company data, user lists, or private customer details stored in the SQL database.
Domain Name System (DNS) attack
A DNS attack is a type of cyberattack in which cyber criminals take advantage of flaws in the Domain Name System to redirect site users to malicious websites (DNS hijacking) and steal data from affected computers. It is a severe cybersecurity risk because the DNS system is an essential element of the internet infrastructure.
Latest cyber threats
The following are the latest cyber threats reported by the U.K., U.S., and Australian governments:
Romance Scams
The U.S. government found this cyber threat in February 2020. Cybercriminals used this threat through dating sites, chat rooms, and apps. They attack people who are seeking a new partner and duping them into giving away personal data.
Dridex Malware
It is a type of financial Trojan malware identifies by the U.S. in December 2019 that affects the public, government, infrastructure, and business worldwide. It infects computers through phishing emails or existing malware to steal sensitive information such as passwords, banking details, and personal data for fraudulent transactions. The National Cyber Security Centre of the United Kingdom encourages people to make sure their devices are patched, anti-virus is turned on and up to date, and files are backed up to protect sensitive data against this attack.
Emotet Malware
Emotet is a type of cyber-attack that steals sensitive data and also installs other malware on our device. The Australian Cyber Security Centre warned national organizations about this global cyber threat in 2019.
The following are the system that can be affected by security breaches and attacks:
Communication: Cyber attackers can use phone calls, emails, text messages, and messaging apps for cyberattacks.
Finance: This system deals with the risk of financial information like bank and credit card detail. This information is naturally a primary target for cyber attackers.
Governments: The cybercriminal generally targets the government institutions to get confidential public data or private citizen information.
Transportation: In this system, cybercriminals generally target connected cars, traffic control systems, and smart road infrastructure.
Healthcare: A cybercriminal targets the healthcare system to get the information stored at a local clinic to critical care systems at a national hospital.
Education: A cybercriminals target educational institutions to get their confidential research data and information of students and employees.


Leave a Reply